Because of Android’s massive user base, programmers have taken a shine. However, as a user, it would be impractical to run apps that require a lot of system resources on phones that can barely handle voice calls. To help out in this situation, android emulator Linux are available.
An Android emulator is software that acts and performs like an actual Android device. It allows Android apps to be executed on a traditional computer. The best part is that it works fine even on older, less powerful PCs. Consequently, we have compiled a list of the top 5 Android emulators for Linux-based platforms.
5 Best Android Emulator Linux (2024)
Because there aren’t many dedicated android emulator Linux, we’ll be installing several x86 Android projects like Bliss OS. To get started, download and run VirtualBox.
Android-x86 emulator for Linux

Android-x86 is an excellent alternative to other phone emulators if you want to run Android games and programs on a computer. You can install the Android OS on its own, but it also offers an ISO that you can use to boot the system into Android without any additional software.
As its name suggests, Android-x86 is optimized for the x86 processor family. Alternatively, you can use the Live CD to launch the program without installing anything. The default interface is reminiscent of Android’s application launcher, but you may optionally use a desktop interface similar to Windows.
The Google Play Store also has a variety of themes available for download. All of Google’s services are fully supported on Android-x86.
Important Android-x86 features:
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth support with GUI
- Bluetooth, G-sensor support
- External storage automount support.
- Theme support to GRUB-EFI
- Preinstalled terminal emulator
Fast software updates also contribute to the stability of this android emulator Linux. The developers released several new features in the first stable Android-x86 release based on Android Pie 9.0. One of these was experimental Vulkan compatibility for more current Intel and AMD GPUs.
How To Install Android-x86 On Linux?
You must download two files, an ISO and an rpm, to install Android-x86 on a Linux desktop.
Booting using ISO
Use ISO to make a bootable USB disk. But before you do that, you should run this command to make sure that you are linking the correct USB device:
$ lsblk
It will list everything that is linked to your computer right now. A note of the device’s name is required for use in the following command.
$ dd if=android-x86_64-9.0-r1.iso of=/dev/sdX
where sdX is the device name for your USB disk.
After a system restart, it will add a new entry to the boot menu.
Booting using RPM
You can use the rpm image using the following command on a Red Hat-based Linux system.
sudo rpm -Uvh android-x86-9.0-r1.x86_64.rpm
On the other hand, if you’re using a Debian-based Linux distribution, you may use the alien software to turn a USB stick into a bootable drive.
sudo apt install alien
sudo alien -ci android-.rpm
To use Android-X86 Emulator on Arch Linux or any distribution based on Arch Linux, you can clone the official AUR package and build it from scratch.
Finally, after the reboot, you may enjoy Android to the fullest.
To use Android x86 on a current Host system, you can use the QEMU Android emulator.
How To Install And Run Android Apps In Android-x86?
You may find and download any program you want from the vast selection available in the Google Play Store for Android, which comes preinstalled on most devices.
AVD (Android Virtual Device)
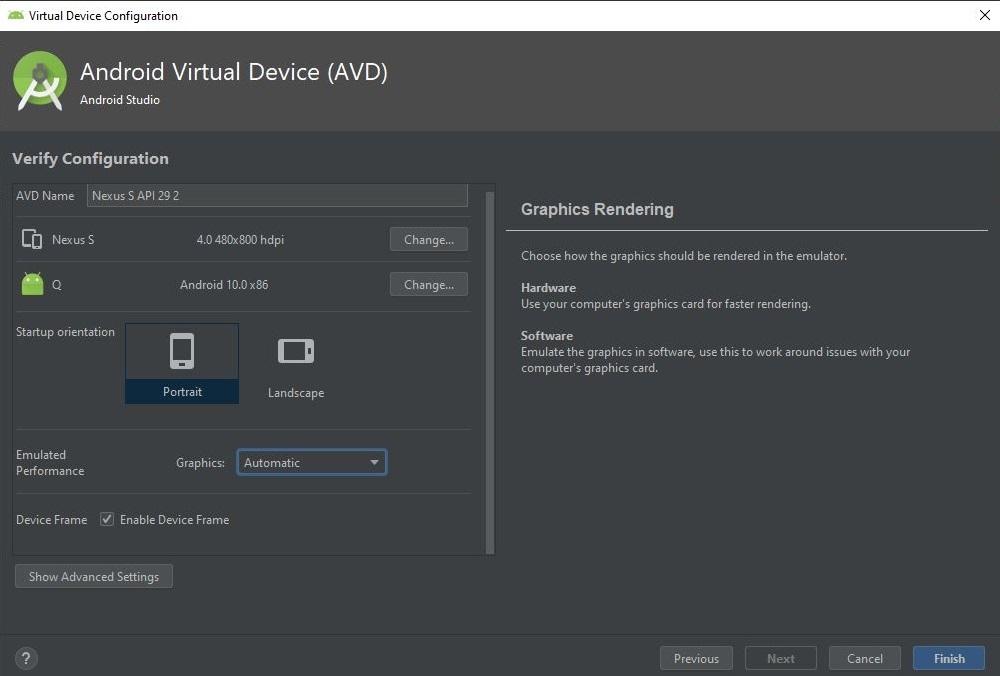
If you’re looking for a reliable Android clone that comes close to mimicking the real thing, go no further than AVD. It comes with the Android Studio integrated development environment (IDE), which you can use to create apps.
It’s possible to simulate everything from incoming phone calls and text messages to varying network speeds, rotation, and other hardware sensors. To get data from or debug an Android app, you can connect external devices to it via USB.
Since Android Studio is a Google product, official help from Google is expected. Additionally, AVD is the best choice for developers looking for a feature-rich code editor.
The programmer can use the GUI or command line of the virtual device during real-world testing. In addition, they can try out AR apps on Android.
Key features of Android Virtual Device:
- Direct Google support
- Easy testing and debugging
- Navigation gestures
- Screenshots & screen recording
- Virtual scene camera and ARCore
You can create several Android emulators for Linux and other devices, such as Android tablets, Wear OS wearables, and Android TV devices.
How To Install Android SDK On Linux?
Android Studio needs to be set up and running before the simulated Android environment can be generated and launched.
Once everything has been set up, you can use the virtual device manager to create as many Android emulators as you like, each with its customized settings.
How To Install And Run Android Apps In AVD?
You can use Google’s offerings. Therefore, you may sign up for a Gmail account and download the app directly from Google’s Play Store.
Genymotion

You will find Genymotion if you look for the best online android emulator Linux. Genymotion can be purchased as a cloud service or installed on a local computer. However, as it does not come with open source and free updates, I have ranked it lower.
However, its consistent support and safety as a proprietary emulator make up for this. And if you’re a developer by trade, I think you should give it serious thought instead of AVD. It also works with the Android Studio IDE, so programmers may use it to create, modify, test, and debug Android apps. You can use the testing framework safely because you can access the ADB.
Moreover, Genymotion android emulator Linux provides full integration for all capabilities, including cellular, Wi-Fi, GPS, and SD card support.
Key features of Genymotion:
- Wi-Fi & GPS
- Camera capture
- Support Android Studio
- Cloud-based and Desktop virtual device
- SMS & Call
You can use the web-based Android emulator to avoid downloading and installing Genymotion Desktop. Genymotion Cloud allows you to play demanding games and apps on a desktop display without the need for any additional software or hardware.
How To Install Genymotion On Linux?
Genymotion requires the desktop edition to be purchased before installation. Alternatively, you can pay for access to the cloud edition and use the android emulator Linux in a browser without downloading or installing anything. The official website can find pricing details for cloud and desktop services.
How To Install And Run Android Apps In Genymotion?
Genymotion is compatible with any Google product available. This means you can run any app designed for Android on your computer.
Bliss OS
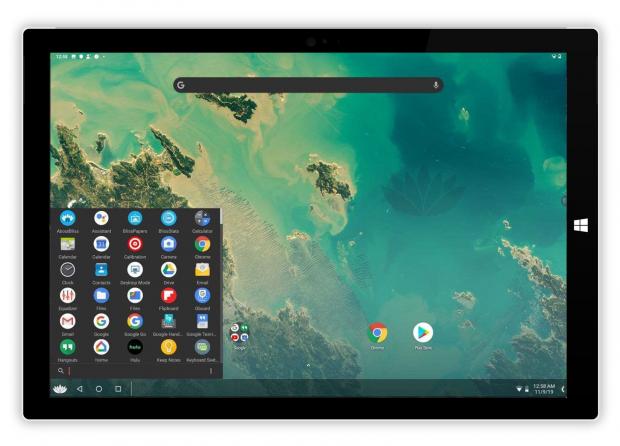
Bliss OS is a viable choice if you are looking for an alternative to Android-x86 based on the ISO format. This allows Android apps to run without a hitch on any Linux computer or tablet and supports booting in both MBR and UEFI modes.
Bliss OS has the most cutting-edge UI in addition to the basic Android functionality. Multiple options for personalization and skinning are included. It’s also possible to switch between a desktop and tablet interface, depending on the launcher you pick.
Bliss OS’s free Android emulator runs popular apps quickly and reliably and does it without cost. To make the most of your device’s display, you can scale the app to fit its dimensions.
Also, Bliss OS may be installed as a custom ROM on Android devices with a bootloader that you can unlock. You should look into it if you’re thinking of rooting your Android device.
Key features of Bliss OS:
- Polished Design
- Network & Wi-Fi
- Google Play Store
- ARM application
- Available for both Mobile & Tablet
Bliss OS, an Android 10-based beta, is available for testing and can run ARM and ARM64-based apps.
How To Install Bliss OS On Linux?
The Bliss OS setup procedure is the same as the Android-x86 setup procedure. Downloading and starting the emulator’s ISO file use the same methods. The beta version of Android 9 Pie is also available for testing.
How To Install And Run Android Apps In Bliss OS?
The process of installing an app on Bliss OS is identical to that of the Google Play Store. The latest and greatest version of BlissOS is available here.
Anbox
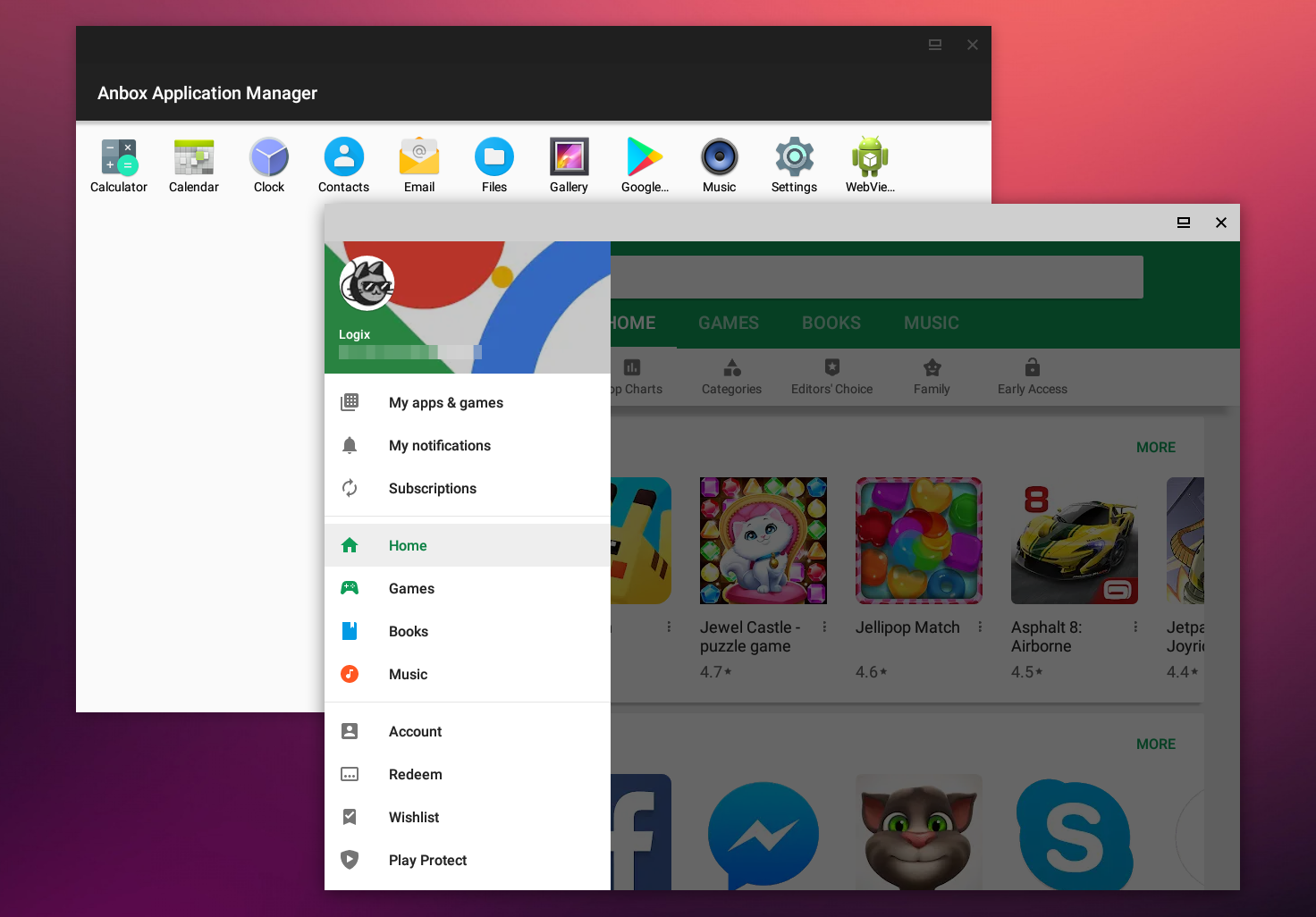
The Canonical company, makers of my preferred and the most widely used Linux distribution, Ubuntu, also developed Anbox. Since Anbox does not work with the Google Play Store, it still comes in last place.
It functions like a compatibility layer, letting you use Android apps on any GNU/Linux distribution. For this reason, you cannot just install the program from the Play Store; instead, you must use the ADB tool to install the APK you downloaded.
Anbox does not create a virtual machine but instead uses the host machine’s kernel and resources to run Android. Therefore, programs operate swiftly and smoothly on Anbox’s free Android emulator.
In addition, Anbox takes an innovative approach to using LXC containers to isolate Android OS from the host computer completely. With its ability to act more like a virtual computer and faithfully recreate the feeling of using a mobile Android smartphone, BlueStacks is among the best Android emulators for Linux.
Key features of Anbox:
- Open-source
- Container-based approach
- Secure and scalable
- APK application support
- Cloud version available
Mobile operating systems, including Ubuntu Touch, Sailfish, and LuneOS, are all available for installation on Anbox. Additionally, Anbox is the best Android emulator for Kali Linux.
How To Install Anbox On Linux?
Obtaining Snap, a program that helps manage your apps is a prerequisite for setting up Anbox.
Type in this command to set up a snap:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install snapd
You can try out Android on a Linux system by running the provided command in the Anbox.
sudo snap install –devmode –beta anbox
How To Install And Run Android Apps In Anbox?
Despite the absence of Google Play services, you can manually install APK files on Anbox. To get the app going, you’ll need to get ADB (Android Debug Bridge) set up on your host system.
To proceed with the command, you can:
$ sudo apt install adb
You can now download the APK file for any program you’d like to install, as all prerequisites have been met. You may download it via Apkmirror and Apkpure.
To get a complete inventory of your system’s Android emulators, simply type the following command.
$ adb devices
To continue, run the installation command below; once complete, the app should be in your Anbox.
$ adb install path/to/my-app.apk
Want more Android Emulators?
I’d also want to mention a few additional excellent Android emulators for Linux. The list includes ARChon, AndyOS, and a plethora of others. However, a few of them are still in the works, and others have limited use.
Other Android OSes exist, such as Prime OS and Phoenix OS, which are based on the x86 architecture; however, they typically use very old versions of the Android OS (Android 7.0 Nougat).
FAQs
How can I run Android apps on Linux without an emulator?
For those who prefer not to use an emulator, Anbox allows running Android apps on Linux. It’s a bit like Wine, except it lets you use Android software on any GNU/Linux machine rather than Windows or Mac software. Android apps are run directly on the host kernel without needing an emulation layer.
Is it possible to use Android apps with Ubuntu touch?
Through Anbox, you may now use Android apps on Ubuntu touch.
Is there a difference between an emulator and a virtual machine?
A virtual Machine, as the name implies, is a software simulation of physical hardware. In contrast, emulators may simulate hardware without using any actual CPU power.
Can I use BlueStacks on a Linux computer?
Unfortunately, you cannot use BlueStacks on Linux at this time. However, comparable solutions that work with Linux exist. You can try out Android-x86, AVD, Genymotion, and Bliss OS if you want to.



